What Are the Most Common Oral Infections
|
Time to read 7 min
|
Time to read 7 min
Oral health is the condition of being healthy and free of diseases that limit the ability of a person to chew, bite and speak or smile. The most common oral infections are facial and mouth pain, teeth loss, teeth decay, oral infections and periodontal or gum disease, and throat and oral cancer.
No matter what age, the oral health of a person is essential for a person's overall health as well as the quality of life and even psychosocial well-being. But many people ignore it. The mouth can reveal signs of nutritional deficiencies or general infections.
Inadequate nutrition, poor oral hygiene habits, and cigarettes and alcohol use are typical risks for developing oral disease.
Here are eight common types of mouth infections :
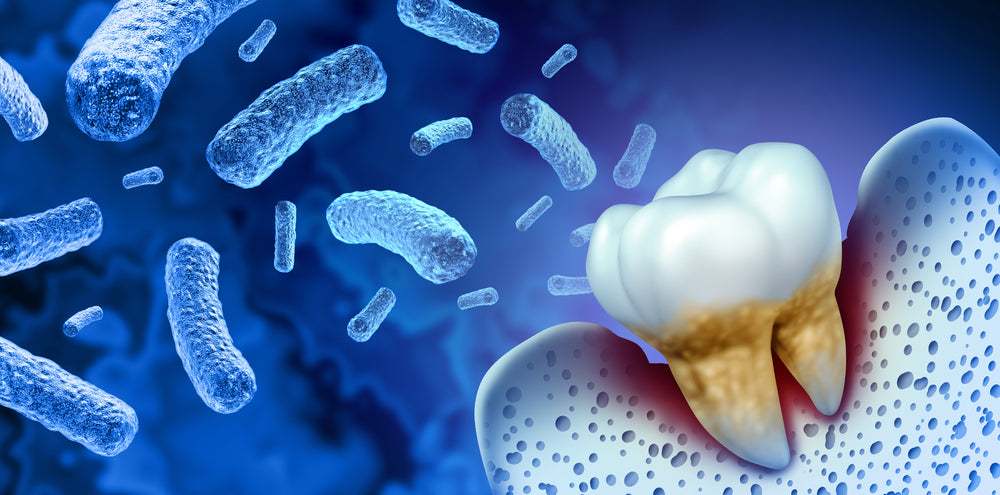
Cavities: Cavities, also known as dental caries, are caused by bacteria that produce acid that attacks the enamel of the teeth.
Gum disease: Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It is caused by bacteria in plaque, a film of bacteria that constantly forms on the teeth.
Cold sores: Cold sores are small, painful blisters that appear around the mouth, lips, or nose. They are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).
Thrush: Thrush is a fungal infection of the mouth caused by the Candida fungus. It can cause white patches on the tongue and inside the cheeks.
It's important to practice good oral hygiene and use Great oral health naturally regularly to help prevent these infections.
There are many types of bacteria that can cause oral infections. Some of the most common ones include Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus sanguinis, and Porphyromonas gingivalis. These bacteria can cause infections such as tooth decay, gum disease, and abscesses. Other bacteria that may cause oral infections include Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Treponema pallidum. It is important to practice good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing regularly, to help prevent the growth of bacteria in the mouth.
Are you looking for what does an oral infection looks like? There are several signs that you may have an oral infection:
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider or dentist as soon as possible to diagnose and treat the infection.
There are many different things that can cause a mouth infection. Some common problems include:
Bacteria: Many types of bacteria can cause infections in the mouth, including Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Neisseria.
Viruses: Viral infections, such as the flu or herpes simplex virus, can also cause infections in the mouth.
Fungi: Fungal infections, such as thrush, can affect the mouth.
Allergies: Allergic reactions to certain foods or substances can cause swelling and redness in the mouth.
Trauma: Injuries to the mouth, such as cuts or abrasions, can lead to infections if they become infected.
Dry mouth: Saliva helps to keep the mouth clean and moist, so a lack of saliva (a condition known as dry mouth) can increase the risk of infections.
Poor oral hygiene: If you don't brush and floss your teeth regularly, food particles and bacteria can build up in your mouth, leading to infections.
If a mouth infection goes untreated, it can spread to other parts of the body and cause more serious health problems. For example, a tooth infection can spread to the jaw and face, leading to abscesses and cellulitis. A gum infection can spread to the neck and head, leading to osteomyelitis (a bone infection) or sepsis (a potentially life-threatening infection of the bloodstream). An untreated throat infection can spread to the ears, causing middle ear infections. It is important to see a dentist or adopt good oral hygiene if you suspect that you have a mouth infection so that it can be treated appropriately.
It can take several days to a week or more for a mouth infection to heal, depending on the cause and the severity of the infection. In some cases, a mouth infection may resolve on its own, while in other cases, treatment with proper oral health care may be necessary. If you have a mouth infection, it is important to follow the treatment plan recommended by your doctor or dentist to ensure that the infection is fully resolved. If you are experiencing severe pain, difficulty swallowing, or difficulty breathing, you should seek medical attention immediately, as these may be signs of a more serious infection that requires immediate treatment. You can use Great oral health toothpaste or mouthwash to get an infection-free mouth.
There are several signs that you may have an oral infection:
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider or dentist as soon as possible to diagnose and treat the infection.
Effective bad breath remedies include:
Gentle and regular scraping of the tongue
Regular oral care practices such as daily brushing and flossing
Professional deep cleanings and plaque removal
The ongoing use of oral probiotics.
One, the probiotics compete with the existing bad bacteria and reduce their presence by “crowding them out”
Two, the probiotics produce BLIS or “bacteriocin-like-inhibitory-substances” which is a technical way of stating that one probiotic strain (bacteria) can produce a substance that inhibits or kills off other bacteria. Three, by working to control gingivitis, gum disease and tooth decay these probiotics reduce the very sources of bacteria-generated odors in the mouth.
Studies have shown a clear reduction in plaque levels and gingivitis symptoms when oral probiotics were administered to patients with moderate to severe gingivitis.


